What is Depression? Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Depression is a common mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of low mood characterized by sadness and lack of motivation that interfere with your everyday activities. It also includes loss of interest in activities you once used to cherish. It leads to a variety of emotional and physical problems and also decreases your ability to function at work and home.
Overview of Depressive Disorder
Depression, also known as clinical depression or major depressive disorder, affects how you feel, think, and behave. It can cause physical and psychological problems, making it hard to do everyday activities. Sometimes, you may feel like life isn’t worth living.
It is a serious medical condition that can worsen without treatment. However, seeking treatment can lead to improvements in symptoms within a few weeks. It is treatable, but it requires long-term treatment.
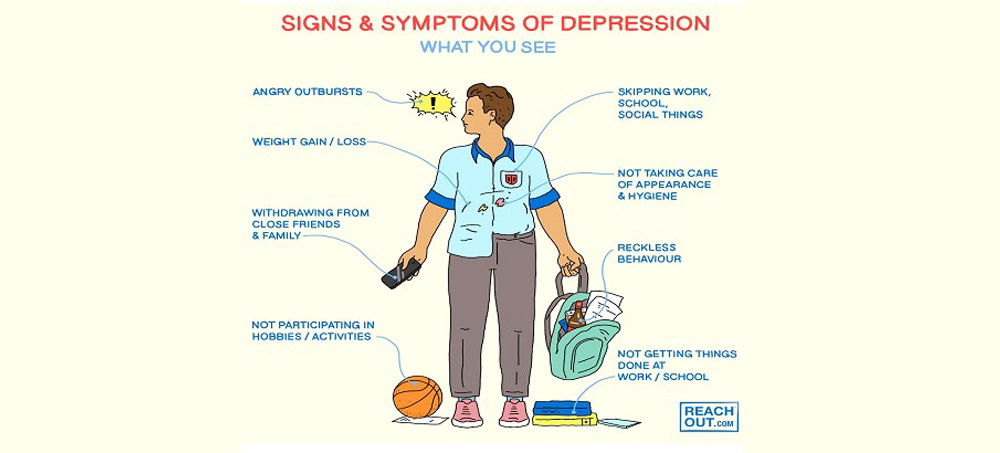
What are Depressive Symptoms?
Its Symptoms vary from individual to individual. They commonly are associated with:
- Feeling of sadness or having a hopeless mood.
- Loss of interest in activities which you used to enjoy.
- Changes in appetite and developing eating disorders like Anorexia Nervosa or Bulimia Nervosa.
- Angry outbursts, irritability, or frustration even over small matters.
- Insomnia (trouble falling asleep) or Hypersomnia (sleeping too much).
- Loss of motivation decreased energy or increased fatigue.
- Increase in pointless physical activities.
- Difficulty in concentrating, thinking, and making decisions.
- Thoughts of hopelessness and suicide.

What are the Common Types?
There are many different types of depression. It can occur due to life events or be a chemical imbalance in the brain.
Major depression
This involved feeling depressive most of the time for two weeks or more.
Persistent Depressive Disorder
This is also known as Dysthymia. To meet this criteria you have to experience depressive symptoms for more than two years.
Bipolar Disorder
It can occur with a mood disorder known as Bipolar Disorder. It is characterized by mood changes that can go from a depressed state to hypomanic or manic states, which is an episode of high energy levels.
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Its occurs most often during the winter months. This is because the daylight is shorter and nights are longer. Conducting daily routines become more difficult. This type of depression usually subsides at the end of the winter.
Psychotic
This is usually occurs with major depression. It includes psychotic symptoms such as having illusions, delusional thinking, or hallucinations.
Postpartum
This type of depression occurs after a woman gives birth to a baby. It can last for weeks or months after childbirth. Hormones are suspected to play a major role in this type of depression along with the psychological and physical stress of being a new mother.
Situational Depression
Its occurs when you are experiencing a stressful life event and are having problems coping with the stress levels. Examples are losing a loved one or divorce. This type of depression will typically be resolved once the stress has decreased.
Atypical Depression
This type is very different from experiencing continuing sadness and other symptoms. It is considered to be more of a pattern-like specifier of depression. Any positive event usually improves your mood if even temporarily.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD):
Also known as a pre-menstrual syndrome. It causes more serious Pre-menstrual symptoms like severe irritability, depression, and anxiety due to a sudden upsurge in hormones.
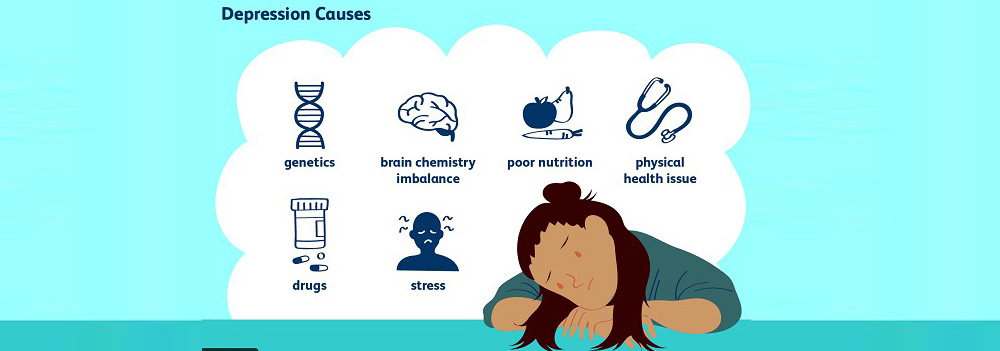
What Causes Depression?
There are numerous possible causes. They can range from biological, genetic, chemical, psychological, and circumstances.
Early childhood trauma:
Some events affect the way your body reacts to fear and stressful situations and cause you to become prone to depression.
Family history
You have a greater chance of developing it if you have a family history of depression or family history of another mood disorder.
Structure of brain:
There’s a greater risk of depression if the frontal lobe of your brain is less active.
Medical conditions:
Certain medical and psychological conditions may put you at higher risk of developing depression i.e. chronic illness, chronic pain, sleeplessness or attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, etc.
Alcohol or drug use:
A history of drinking or doing illicit drugs can greatly increase your risk level for developing depression.
Biological causes of depression:
It is likely that in clinical depression the neurotransmitter functions that carry signals from one part of the brain to the next is disrupted. It is also seen that increase or decrease in serotonin, noradrenaline, and dopamine (i.e. hormones that are regulators of mood) can also cause depressive mood.
What are the Risk Factors for Depression?
Depression is usually observed when someone is in their twenties or thirties, but it can occur at any age. Women are more likely to experience it as compared to men. Some other risky factors include:
- Specific personality traits such as low self-esteem, being too dependent, self-critical, or pessimistic.
- Traumatic events, such as suffering from physical or sexual abuse, death of a loved one, a difficult relationship, or financial issues.
- Close relatives with a history of depression, bipolar disorder, alcoholism or suicide.
- History of other physiological or psychological disorders such as anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder.
- Abuse of alcohol or illicit drugs.
- Serious illness such as cancer, heart disease, etc.
- Certain medications such as some high blood pressure medications, sleeping pills, etc.
Complications of Depression:
If it is not treated it can result in serious physical and psychological issues that affect every area of your life. Examples are:
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain, which can lead to other problems.
- Body aches or physical illness
- Alcohol or drug addiction
- Panic disorder, anxiety, or antisocial behavior
- Relationship difficulties and work problems
- Social isolation
- Suicide attempts
- Self-harming behaviors
Committed to helping
people who want to help themselves
Diagnosis of Depression:
It involves a consultation and physical exam. Sometimes, a blood test is needed to rule out medical conditions like thyroid issues or heart disease. The assessment looks at symptoms, medical and family history, and environmental factors. If depression is found, the diagnosis includes the type and severity.
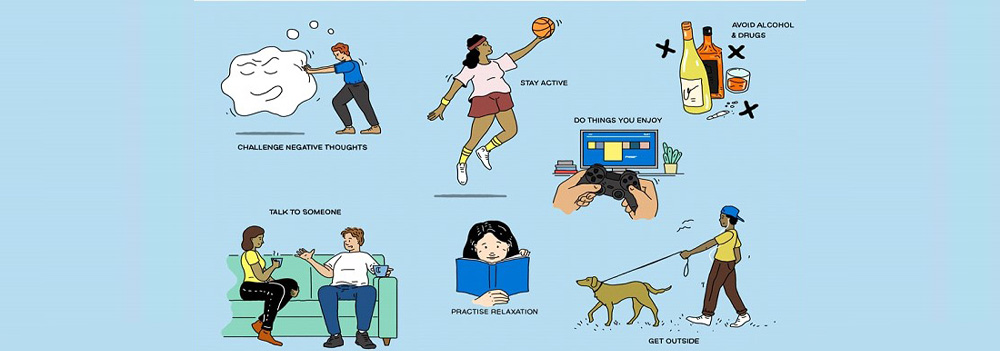
How to Prevent Depression?
Here are some strategies that may help to prevent it:
- Management of stress, to increase your strength, resilience and to boost your self-esteem.
- In times of crisis reaching out to family and friends to help you go through difficult times.
- Considering attending therapy which helps to work through the depression and prevent re-occurrence of symptoms.
- Seeking treatment at the earliest stage of the problem helps to prevent it from getting worse.
- Keeping a track of your triggers and learning to avoid or manage them.
- Making some leisure time for yourself.
- Regular exercise
- Getting plenty of sleep
- Spending some time in nature
- Practicing gratitude
- Keeping your focus on the brighter side
When to Seek Help?
You should seek medical help if you are facing following symptoms lasting for two weeks or more:
- Sleep problems
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplainable mood changes
- Sudden loss of interest in almost everything
- Feelings of hopelessness or helplessness
- Palpitations (irregular heartbeat)
- Suicidal thoughts
- If you are not feeling like yourself and want help to understand why to make an appointment to visit your health care provider. It is very important, to be honest, so they can completely understand what is wrong and get a clear understanding of what you are feeling. They will help decide what is the best course of treatment for you.
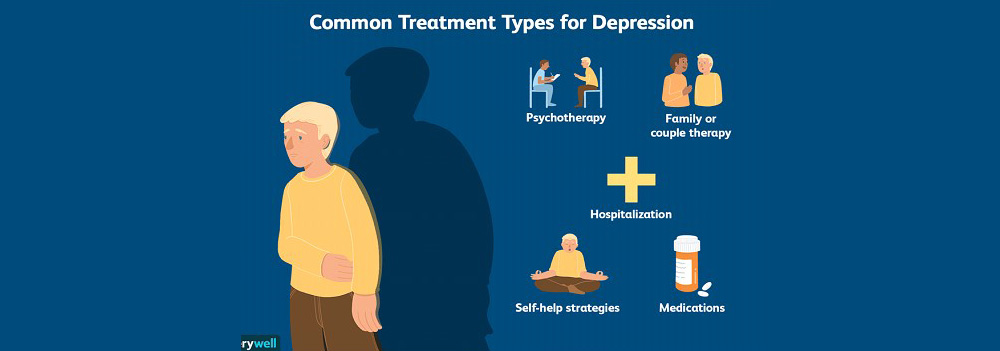
Common Treatment:
This is among the most treatable mental health problems. Between 80% to 90% of people eventually respond well to treatment. Almost all patients gain some relief from their symptoms. Different approaches like psychotherapy, medication, and natural remedies are used to treat depression.
Medications:
- Anti-depressants, which include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly used to treat depression.
- Anti-anxiety medications: These include drugs which can help to reduce the symptoms of anxiety.
- Mood stabilizers: When antidepressants do not work by themselves, a mood stabilizer might help to decrease emotional instability.
- Vitamins: Deficiency of vitamin B-6, vitamin B 12, and vitamin D are seen to increase depression symptom therefore the supplementation of these vitamins is helpful.

Psychotherapy:
Speaking with a therapist can help you learn about the triggers and thought process that promotes depressive symptoms. The therapist will assist in teaching skills to cope with negative and depressive feelings. You may also benefit from family or group therapy sessions.
Natural remedies:
- Exercise
- Stress management
- Meditation
- Use of essential oils like lavender oil and bergamot oil which have anti depressive properties
- Aromatherapy
