Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Guid
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), is known by several other names like shell shock, delayed post-traumatic stress disorder, delayed stress syndrome, delayed PTSD symptoms, battle fatigue syndrome, post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSS), and railway stress syndrome. It is a serious psychological condition that can develop after you have witnessed or experienced a traumatic or extremely stressful event that may include a perception of danger, life-threatening, or distressing shock. PTSD is a long-term consequence of a traumatic experience that leads to anxiety, fear, feeling helpless, panic, or horror.
Overview of PTSD
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is usually activated by experiencing or witnessing a disturbing life event. The majority of individuals who go through traumatic events might have short-term difficulty adjusting and coping. Other reactions might include fear, shock, anger, nervousness, and guilt, etc. With time and good self-care, these Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder symptoms usually get better. For a person with complex PTSD symptoms, the feelings are persistent and can increase to a level where it negatively impacts day-to-day functioning.
People with complex PTSD signs and symptoms that last longer than one month and they are not able to function as they did before the distressing event. Getting an effective psychological evaluation and treatment, or potential medications, after the activation of PTSD signs and symptoms can be helpful to reduce the Post Traumatic Stress Disorder symptoms and improve daily life functioning.

What Causes Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder can occur after an extremely frightening or stressful event or after a persistent traumatic experience. PTSD symptoms and signs develop in about 1 in 3 people who go through a severe traumatic experience. Signs of PTSD in women are more common than the signs of PTSD in men. The types of events that can lead to severe PTSD symptoms include:
- severe accidents
- sexual assault
- childhood or domestic abuse
- exposure to a traumatic event at home, school, or work
- serious health-related issues
- childbirth experience or the experience of losing a baby
- conflict or war
- mental or physical torture
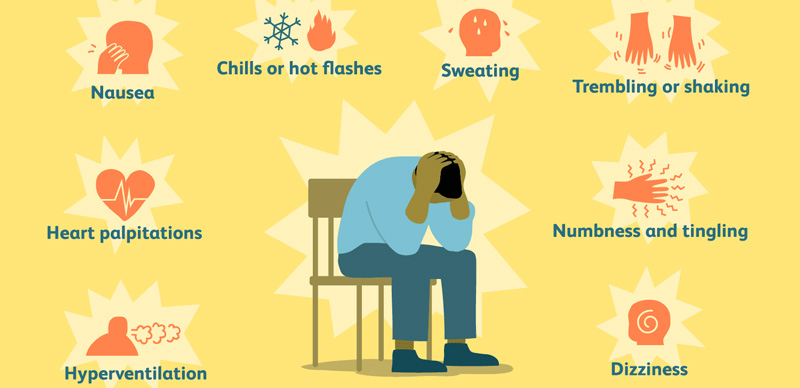
What are the Different Types of PTSD Symptoms?
Symptoms of traumatic stress disorder are divided into three categories:
Cognitive symptoms
- Agitation
- Concentration issues
- Self-harm
- Lack of positive emotions
- Nightmares
- Flashbacks
- The feeling of being overwhelmed
Physical symptoms
- Increased startle response
- Excessive sweating
- High blood pressure
- Higher heart rate
- Sleeping problems
- Breathing issues
- Migraines/headache
Behavioral symptoms
- Hyper alertness
- Detachment
- Withdrawal
- Drug abuse
- Alcohol consumption
- Disciplinary/management issues
Committed to helping
people who want to help themselves
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Types – PTSD Types
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a multifaceted disorder with several different causes and consequences. Research has shown the existence of different types of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder that need different methods of treatment.
Normal Stress Response
Normal stress response occurs before PTSD starts, but it may not lead to higher stages of the disorder. Events such as surgeries, injuries, accidents, severe illnesses, and other sources of pressure and stress can all give rise to a normal stress response.
Acute Stress Disorder
Acute stress disorder (ASD), occurs in people who have been exposed to a frightening event. For example, natural disasters, loss of loved ones, loss of a job, etc. If it is not treated then over time it can lead to the development of PTSD.
Uncomplicated PTSD Symptoms
Uncomplicated PTSD Symptoms are associated with one major distressing event and are the simplest form of PTSD to treat. Uncomplicated PTSD Symptoms include nightmares, flashbacks of the incident, derealization, irritability, and mood swings.
Complex PTSD Symptoms
Complex PTSD Symptoms are caused by several distressing events. This type of PTSD is common with experiences of domestic violence, war, violence in a community, or sudden loss of a loved one or an asset. Complex PTSD Symptoms involve anxiety, panic, behavioral issues like sexual impulsivity, aggression, or substance abuse, etc.
Comorbid PTSD Symptoms
Comorbid PTSD Symptoms involve co-occurring disorders. It includes more than one mental health issue and is often linked with substance abuse. Comorbid PTSD is very common because people may have more than one issue at a time. Best results for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder treatment are achieved when both mental issues and co-occurring PTSD are treated together by a professional.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment – PTSD Treatment
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder affects everyone in a different way. A specific mental health treatment that is tailored to someone’s specific needs is very important. A PTSD treatment modality that works for one person may not work for another. The PTSD treatment includes psychotherapy/talk therapy, medication, or both.
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that has steadily been found to be very effective in treating PTSD and its focus is trauma-based. The skills learned during this course of treatment are practiced repeatedly to help stop the symptoms of trauma. The types of CBT treatment that work well for PTSD are Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), Prolonged Exposure (PE), and Stress Inoculation Training (SIT).
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Medications
Different medications can help reduce Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder symptoms. Anti-depressants might help control depression and anxiety symptoms such as worry, sadness, anger, and feeling of emptiness inside. Some medications can also help with anxiety, nightmares, and sleep problems.
Committed to helping
people who want to help themselves
