What is Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a serious personality disorder characterized by continuous instability of the emotion regulation system, interpersonal relationships, impulse control, and self-image. This long-lasting and severely distressing disorder includes both genetic and environmental factors.
Overview of BPD
Borderline Personality Disorder affects about 1 to 2% of the world population or 10% of individuals per country. This disorder has a high mortality rate compared to any other mental health issue because suicidal tendencies or attempts are 50% higher than other individuals. Individuals require more extensive BPD treatment plan and management than those having other psychological disorders. BPD traits may differ for individuals. So, it’s important for you to consult some experienced psychologist to know about your BPD traits.
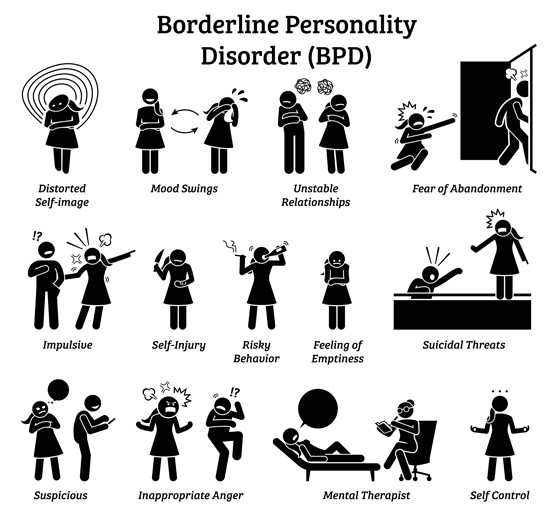
BPD Symptoms:
There are lots of BPD symptoms – signs of BPD but we’ll talk about 4 major BPD symptoms. Here is the BPD Symptoms list:
- Emotional instability is commonly known as affective dysregulation
- Troubled patterns of perception or thinking, also known as cognitive distortions
- Impulsive behavior
- Strong but unstable relationships with others
Individuals with BPD Symptoms might go through a range of intense and negative emotions, such as:
- Aggression
- Sadness
- Embarrassment
- Panic
- Terror
- Feelings of emptiness that are long-lasting
Causes of Borderline Personality Disorder:
The major cause of Borderline Personality Disorder is not known. There is research that suggests it is a mixture of genetics and environmental factors.
Risk factors for Borderline Personality Disorder:
- Brain structure:
There is research that suggests there are differences in the structure and function of the brain, especially in the area that controls impulses and the regulation of emotions. Nonetheless, it is still not certain if these differences in the brain are the result of having BPD, or if they are the cause of the disorder.
- Family history:
Having a parent or sibling with BPD may increase the risk of developing the disorder.
- Negative past experiences:
Many people who are diagnosed with the disorder have a history of child abuse, negligence, trauma, or were separated from their parents at an early age. On the other hand, it is not a necessary criterion because not all people with the disorder have experienced trauma, and conversely, many people who had such experiences do not develop the disorder.
Complications of BPD:
- Drug or alcohol abuse
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Difficulties with relationships
- Eating disorders (i.e. anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa etc.)
- Legal or financial issues
- Problems at school and work
- Self-harming attitudes/behaviors
- Social isolation
- Tense family relationships
- Suicidal tendency
Borderline BPD:
Affective Criteria:
- Unsuitable intense rage or difficulty controlling aggression (e.g., frequent angry outbursts, physical fights, etc.
- Long-lasting feelings of emptiness
- Emotional instability (e.g. irritability, anger, or anxiety lasting for a few hours and seldom for more than a few days.
Cognitive Criteria:
- Persistent stress-linked severe dissociative symptoms
- Identity disruption persistent with an unstable sense of self
- Impulsivity
- Recurrent suicidal tendencies and self-harming attitude/behaviors
Interpersonal Criteria:
- Desperate efforts to escape real or imaginary neglect from others.
- Unstable but strong social relationships are characterized by extremes between fantasy, idealization, and devaluation of others.
Treatment of BPD:
Psychotherapy:
Research shows that the most effective therapeutic treatment modality to help manage Borderline Personality Disorder symptoms is Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT). This Borderline Personality Disorder treatment includes individual, group, and family sessions. The problem is that many insurance companies do not cover this type of therapy because the individual is going to have BPD treatment several times a week.
Another form of Borderline Personality Disorder treatment is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
Borderline Personality Disorder Treatment goals work on the individual gaining an understanding about past and present issues regarding their relationships with family members or others, and treating the impulsive negative behavioral patterns.
Borderline BPD:
There are many BPT Medications also known as BPD Medications. Here is the common BDP Medications list:
- Anti-depressants do help with depressive BPD symptoms
- Selective Serotonin uptake inhibitors (SSRI) to create the sense of relaxation
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors for anxiety and depression
- Tricyclics for management of shifts in moods
Other BPT Treatments
Hospitalization might be required if suicide attempts or self-harming behaviors are present.
